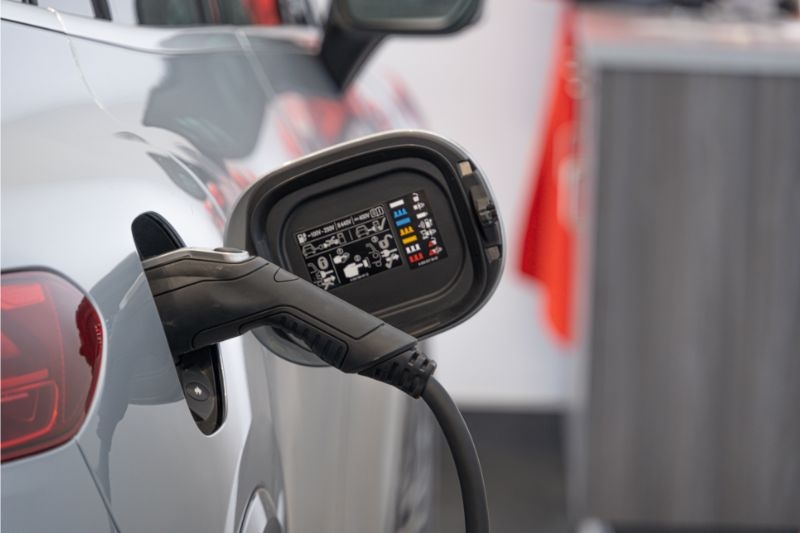
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention in recent years as a sustainable transportation option. With the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change, many countries, including the UK, are encouraging the adoption of EVs. However, the success of electric vehicles relies heavily on the availability and accessibility of a robust charging infrastructure. In this article, We will assess the current state of the electric vehicle charging infrastructure in the UK, analyze the challenges and barriers that hinder widespread adoption, explore government initiatives and policies to support its development, discuss key players in the market, examine different types of charging stations and their features, and look into future trends and advancements in the field.
Challenges and barriers to widespread adoption of electric vehicles
While the UK has been making strides in electric vehicle adoption, there are still barriers that hinder widespread acceptance. One of the main challenges is the upfront cost of electric vehicles. Although the prices have been decreasing, EVs are generally more expensive than their conventional counterparts. This price difference, along with concerns about range anxiety and charging infrastructure availability, creates a barrier for many potential buyers.
Another challenge is the limited range of some electric vehicles. Although newer models are offering better range capabilities, there is still a perception that EVs are not suitable for long journeys. The need for more charging stations, particularly rapid chargers, along major road networks is crucial to address this concern. Additionally, the time it takes to recharge an electric vehicle is still longer compared to refueling a traditional car, although advancements in fast charging technology are reducing this gap.
Government initiatives and policies to support the development of charging infrastructure
Recognizing the importance of a reliable charging infrastructure, the UK government has implemented various initiatives and policies to support its development. The Office for Zero Emission Vehicles (OZEV) has been instrumental in driving the growth of EVs and charging infrastructure. OZEV provides grants for the installation of domestic and workplace chargers, making it more affordable for individuals and businesses to transition to electric vehicles.
Additionally, the government has set a target to ban the sale of new petrol and diesel cars by [insert year], further incentivizing the adoption of electric vehicles. This ambitious goal sends a clear signal to automakers, charging infrastructure providers, and consumers that the future of transportation is electric.
To encourage the expansion of the charging infrastructure, the government has also launched the Rapid Charging Fund, which aims to accelerate the deployment of rapid chargers along major road networks. This initiative will help address range anxiety and promote long-distance travel with electric vehicles.
Different types of charging stations and their features
Electric vehicle charging stations come in different forms and have varying features to cater to the needs of different users. The three main types of charging stations are rapid chargers, fast chargers, and slow chargers.
Rapid chargers are the fastest charging option available and are typically found at motorway service stations. They can charge an electric vehicle up to 80% in around 30 minutes, making them ideal for long-distance travel. Fast chargers are commonly found in urban areas, workplaces, and shopping centers. They can charge an EV in a few hours, providing a convenient option for those who park their vehicles for an extended period. Slow chargers are the most common type and are often used for overnight charging at home. They have a lower charging capacity but are sufficient for daily commuting needs.
Each type of charger has its advantages and disadvantages. Rapid chargers offer quick charging times but require more powerful infrastructure and may have a higher cost per kilowatt-hour. Fast chargers strike a balance between charging speed and infrastructure requirements, making them suitable for both urban and suburban areas. Slow chargers are the most cost-effective option for home charging but may not be suitable for those who require frequent long-distance travel.
Advantages and disadvantages of different charging options
Rapid chargers have the advantage of providing quick charging times, making long-distance travel more feasible. They are also typically located at motorway service stations, which offer additional amenities such as restrooms and food options. However, rapid chargers require more powerful infrastructure and are generally more expensive to use compared to other charging options.
Fast chargers are a versatile option, suitable for both urban and suburban areas. They can charge an electric vehicle in a few hours, providing a convenient charging solution for those who park their vehicles for an extended period. Fast chargers are often found in shopping centers, workplaces, and public parking lots, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles while running errands or during working hours. However, they may not be suitable for long-distance travel, as the charging time is longer compared to rapid chargers.
Slow chargers are the most cost-effective option for home charging. They are easy to install and require minimal infrastructure modifications. Slow chargers are ideal for overnight charging, ensuring that the vehicle is fully charged by the morning. However, they have a lower charging capacity and are not suitable for those who require frequent long-distance travel.
Future trends and advancements in electric vehicle charging infrastructure
The future of electric vehicle charging infrastructure looks promising, with several trends and advancements on the horizon. One significant development is the improvement in charging speeds. Advancements in technology are enabling faster charging times, reducing the time it takes to recharge an electric vehicle. This will address one of the main concerns of potential EV buyers and make electric vehicles even more convenient for daily use.
Wireless charging is another exciting trend in the charging infrastructure market. This technology eliminates the need for physical cables and connectors, allowing electric vehicles to charge simply by parking over a charging pad. Wireless charging offers a seamless and user-friendly experience, making it more convenient for EV owners to charge their vehicles.
The integration of renewable energy sources into the charging infrastructure is also gaining traction. Solar-powered charging stations are becoming more common, harnessing clean energy to charge electric vehicles. This not only reduces the carbon footprint of charging but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the transportation sector.
The role of renewable energy in powering electric vehicle charging stations
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in powering electric vehicle charging stations. By utilizing clean energy sources such as solar and wind power, charging infrastructure can minimize its environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable transportation system. Solar-powered charging stations, in particular, have gained popularity due to their ability to generate electricity directly from the sun.
Solar panels installed on the roofs of charging stations capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This renewable energy is then used to charge electric vehicles, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to being environmentally friendly, solar-powered charging stations can also generate revenue by selling excess electricity back to the grid.
Wind power is another renewable energy source that can be harnessed to power charging stations. Wind turbines located near charging infrastructure sites can generate electricity, which is then used to charge electric vehicles. This approach further diversifies the renewable energy mix and ensures a steady supply of clean energy for charging needs.
Conclusion and outlook for the future of electric vehicle charging infrastructure in the UK
In conclusion, the electric vehicle charging infrastructure in the UK has come a long way, but there are still challenges to overcome. The availability and accessibility of charging stations, along with the consistency of payment systems, need to be improved to encourage widespread adoption of electric vehicles. The government’s initiatives and policies, along with the efforts of key players in the market, are instrumental in addressing these challenges and driving the development of a reliable and user-friendly charging infrastructure.
Looking ahead, the future of electric vehicle charging infrastructure is promising. Advancements in technology will lead to faster charging times and more convenient charging options, making electric vehicles even more viable for daily use. The integration of renewable energy sources into the charging infrastructure will contribute to a greener and more sustainable transportation system. With continued support from the government, private sector investments, and advancements in technology, the UK is well-positioned to power the future of electric vehicles and create a cleaner and greener transportation landscape.